Continuous Glucose Monitoring Device Adhesives
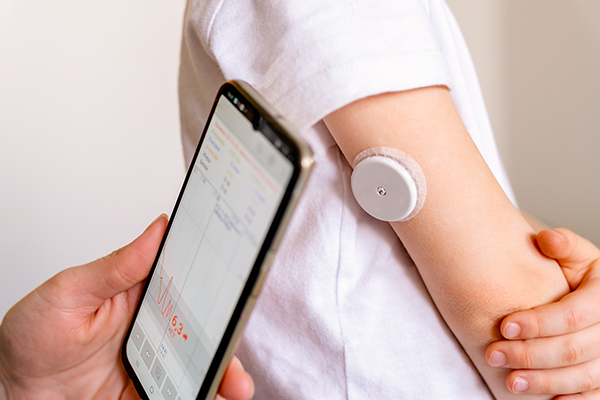
Blood glucose monitoring devices include technology that utilizes test strips for fingertips, blood-free continuous glucose monitoring systems (CGM) worn on the upper arm to the abdomen, and subcutaneous implants. The ability to measure glucose levels through blood or interstitial fluids improves the health and wellness of many individuals.
Continuous glucose monitor accuracy is key to providing patients with a seamless diabetes management experience. These CGM systems are designed to provide real-time glucose data, enabling users to make informed decisions and understand their health. As the need and demand for continuous glucose monitoring devices increase, healthcare providers, manufacturers, and designers of this technology need expert and reliable suppliers to provide all patients with a seamless diabetes management experience.
Since 1998, Polymer Science has provided medical-grade skin contact materials including adhesives, coatings, and tapes. Partners rely on our experience and customer-focused processes when planning continuous glucose monitoring products and seeking out the ideal skin contact adhesives for CGM accuracy, comfort, and durability.
Key Considerations of Continuous Glucose Monitoring Devices
Patients wear blood glucose monitoring devices discreetly instead of relying on resources like conventional fingertip test strips.
A Continuous Glucose Monitoring System (CGM) monitors blood sugar (glucose) levels continuously in real-time throughout the day and night. The glucose sensor, a tiny electrode inserted under the skin, measures the glucose levels in the tissue fluid. It is connected to a transmitter which sends the information wirelessly to a monitoring device. This makes it easy to determine whether or not the glucose levels are too high or too low.
The success of glucose monitoring devices relies on dependable performance, ease of use, and discreet design. A few key considerations of CGM designs include:
- Accurate CGM readings
- Consistent contact of CGM sensors
- Reliable adhesion for extended wear
- Hypoallergenic contact for skin sensitivity and skin irritation of patients
- Environmental factors including water, sweat, and intense exercise
Advantages of Continuous Glucose Monitoring versus Test Strips Devices
Blood glucose monitoring devices that use test strips have key disadvantages. Most notably, a blood glucose meter requires resources including test strips and devices. Another common issue is the discomfort of testing. Finally, there is limited data to aid patients and caregivers in adjusting diet, medication, and activities that adversely impact blood sugar levels.
Diabetes care that provides continuous and dynamic information about glucose levels allows individuals to track blood glucose levels in real-time. CGM sensors rely on interstitial fluid reducing the discomfort of blood.
Minute-to-minute glucose readings available within a smartphone application help avoid hypoglycemia. Understanding how different factors such as food, physical activity, and other stressors impact glucose levels can improve quality of life.
With diabetes technology changing rapidly, emerging advantages of CGM include identifying glucose trends and patterns. Both individual users, caregivers, and medical experts can optimize management strategies using this diabetes technology.
With alerts, notifications, and the ability to review data, new continuous glucose monitoring provides extensive information to determine insulin dosage, the timing of meals, exercise routines, and other lifestyle modifications to achieve optimal glucose control.
There are distinct advantages of Continuous Glucose Monitoring (CGM) instead of traditional glucose testing strips. Clearly, the ease of use and immediate insight into glucose values through smartphone apps and other technology is convenient. This is the primary reason non-diabetic users are interested in CGM system technology.
The increasing adoption of CGM is aided by its effectiveness in older populations. As more adults with type 1 diabetes (T1D) or insulin-using type 2 diabetes (iT2D) are at high risk for severe hypoglycemic episodes, CGM and other diabetes technology can help prevent severe incidents like falls before they occur. For instance, consistent CGM use has been demonstrated to improve glycemic control and reduce SH in patients over 65 years old. Advances in healthcare have improved the outcomes and lifespan of many individuals with T1D and iT2D. Continuous blood glucose monitoring allows these individuals more freedom and improved quality of life.
As in older patients, younger patients are less reliant on resources when using CGM devices. Medical wearables worn 24/7 aren’t forgotten on the way home from school, and individuals don’t have to interrupt social activities to test blood glucose.
While these systems are particularly beneficial for individuals with type 1 diabetes, type 2 diabetes, and those requiring intensive insulin therapy, diabetes technology has a wider market emerging. The capability of diabetes technology to quickly deliver comprehensive insights into glucose tends to enable individuals to achieve better control than at any other time. In fact, this technology has been adopted by non-diabetic uses including those focused on fitness and professional athletes.
Skin Contact Adhesives in Continuous Glucose Monitoring
Improving CGM accuracy, durability, and ease of use will be key to increasing the viability of a product design as popularity and use increase across the industry. Choosing the proper adhesive helps to reduce the risk of erythema, dry skin, hyperpigmentation, and other skin reactions. But there are challenges in selecting the ideal adhesive for any medical wearable device.
Polymer Science worked with the leading CGM makers and developed silicone gels for CGM device fixation. Working with development engineers and combining the newest silicone formulations with our coating expertise on fabric backings, we developed skin-contact silicone adhesives with the following characteristics:
- Wear time above 14 days with constant adhesion profile
- Hypoallergenic
- Waterproof for the more active users
- Atraumatic removal
- Resistant to bacterial growth
All of these qualities aid directly in facing the common challenges of CGM devices for people wearing devices on their skin 24 hours a day, 7 days a week. This increases the risk that people will develop allergies to the commonly used acrylic adhesives.
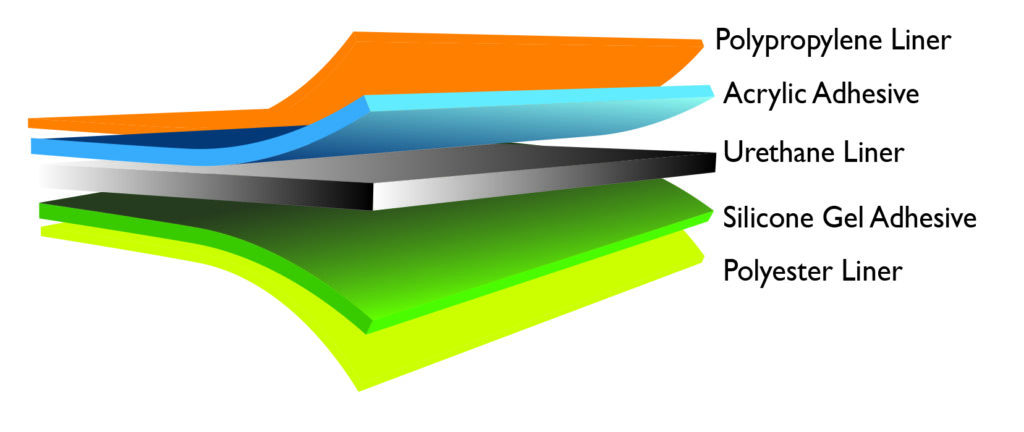
Polymer Science, Inc. has developed a solution to negate that problem from occurring by utilizing our multi-layer construction with a skin contact silicone gel adhesive layer (as shown in the technical illustration below).
Easy-to-apply adhesives, hypoallergenic, long wear times, and consistent contact for CGM sensors improve user experience and increase the long-term success of continuous glucose monitoring devices.
Working with Polymer Science
This is a primary example of the work Polymer Science provides our partners. Our design team works quickly to provide the solutions you need, allowing your project to expeditiously move from conception to production. Download our complete CGM-Brochure.
There are many challenges to consider to avoid the troubleshooting lists compiled by medical professionals.
Our team consists of engineers and technical staff with decades of experience as a leader in medical-grade adhesives. Our state-of-the-art equipment provides the capability to customize width, minimize waste, and offer lower minimum order quantity.
We also offer standard or customized constructions. As diabetes technology advances, working with Polymer Science aims to improve the outcomes for designers, manufacturers, caregivers, and most importantly, the users of CGM devices.